Over the past few years, AI healthcare software has advanced. It has gotten more accurate and more sophisticated. However, the integration of these algorithms into the clinical practice of disciplines like radiology remains challenging.
One of the main problems is the different integration options, or lack thereof, available for the users. Not every AI radiology vendor offers the same possibilities, which makes it challenging to understand who provides what. Additionally, for people that are not familiar with the technicalities of installation processes, most options can seem quite similar, which makes the decision making process even more difficult.
In this blog post we will tackle the most important things to ensure a smooth AI radiology integration. Are you curious about the pros, the cons or the technicalities of onsite installations and cloud solutions and the differences between them? Then, keep on reading!
What is important for AI radiology software integration?
The most important thing to look at when deciding on an AI radiology software is its compatibility with your PACS, your scanners and your programs. Changing the whole radiology workflow to match a new software can be very expensive and time consuming, so we suggest looking into compatible options from the get-go.
To make sure the integration will be smooth and seamless, it is essential to involve the right people. Make sure of involving IT personnel, especially the ones that are going to carry out or support the installation, by, for example, having them attend the demos and ask the more technical questions to the vendor. That will be the easiest way of making sure the integration process will be possible and successful.
Moreover, ensure that the IT personnel can have a direct line of contact with the vendor’s service and installation team to ask these specific technical questions to get the most accurate answers in the least amount of time and without communication interferences caused by having different people, that might not be in tune with the technical side of things, be part of the technical conversation.
Once the decision has been made, a successful integration will depend on the connection of incoming scans and other information (coming from the clinic’s scans or PACS) to the software and the connection of the outgoing reports and measurements to the PACS where the involved professionals will have access to them.
Integration methods: physical workstation, a node on the cloud or a hybrid option?
Physical workstation
Installing the AI software on a physical workstation onsite has some clear benefits. It is an easy-to-realize integration, since it is only necessary to install the AI radiology software on the workstation. All data will remain within the clinical facility, thereby all privacy and data protection problems can be avoided.
However, this type of integration will just add another program to the radiology workflow increasing the radiologist’s workload. Additional insights may be generated from the AI analysis, but the user can only assess scans on the dedicated workstation. Hence all hospital sites will need a separate installation. 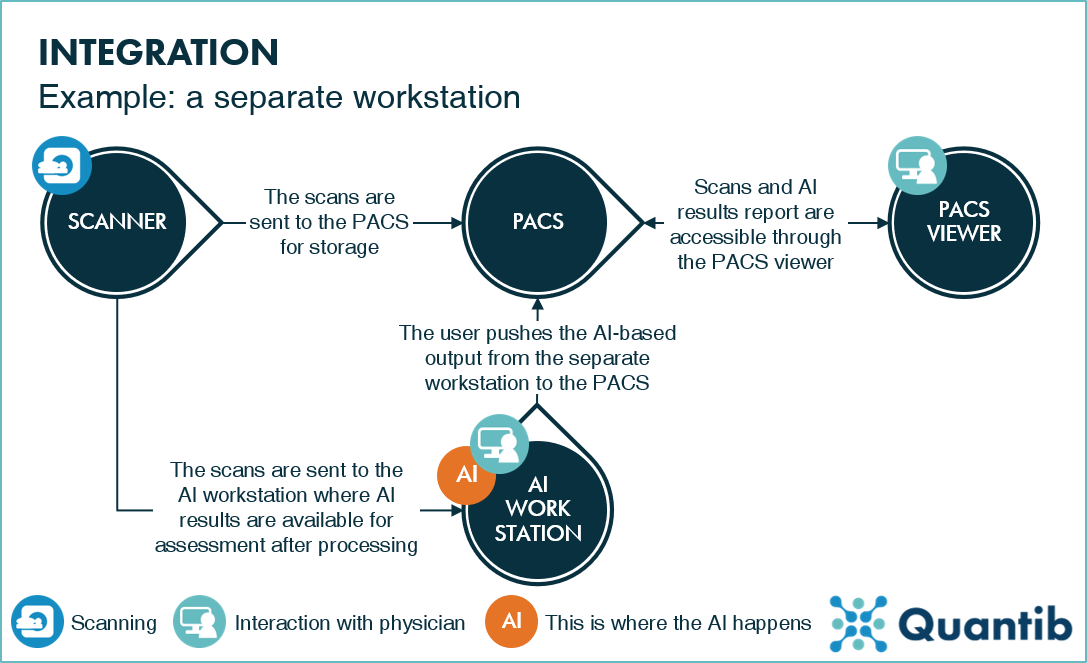
Figure 1: An example of a radiology workflow involving a separate AI workstation.
Fully automated software on the cloud
This integration is very easy to use. The AI software will be installed on a server, also called a node, on the cloud located outside of the clinical facility. The scans are sent to the cloud where the AI software will process them, and the results will be sent back to the PACS. Therefore, this integration requires low effort from both the radiologists and the IT department of the hospital. The crucial element is to (automatically) send the scans to the node and have the node send it back to the PACS in a way that all information ends up in the right place.
On the other hand, this type of integration has some disadvantages. Firstly, the solution is fully automatic, therefore, the radiologist has no chance of editing or validating the information that will appear on the report (e.g. segmentations, measurements or results). This also puts more weight into the quality of the algorithm the software uses to make sure the results are up to the clinical standard.
Secondly, the processing of the scans is done by another entity which will have a processing time that might slow down the radiologist’s workflow (depending on the vendor it could be any time from 15 minutes up to 24 hours). This becomes even more bothersome if something goes wrong with the processing and the scans need to be resent, taking, in the worst case scenario, another 24 hours before the radiologist get the results back.
Lastly, because the processing is done outside the hospital network, this setup is much more complex when it comes to data protection and security regulations. Hence why this integration is generally considered less safe than other options. 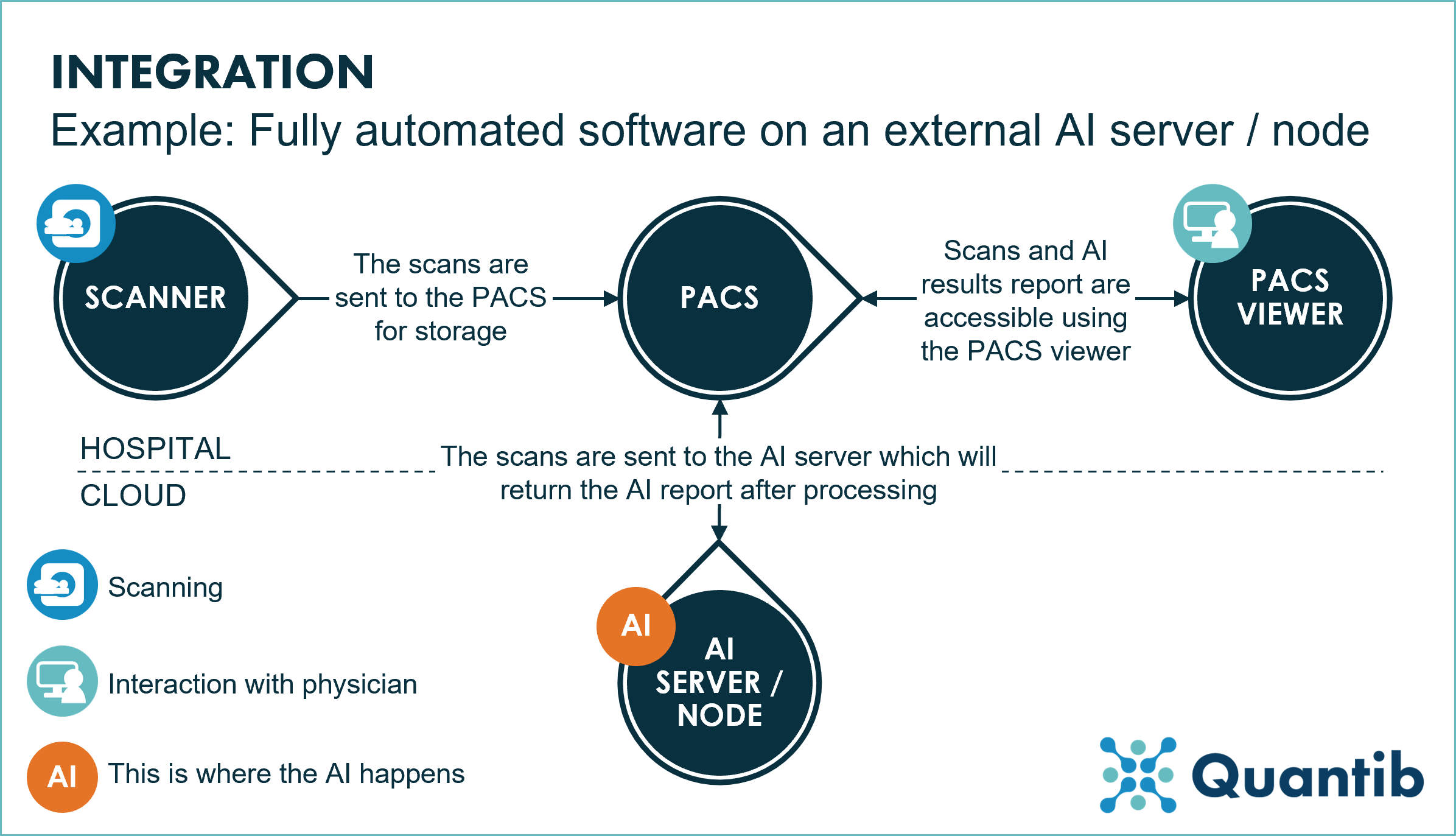
Figure 2: An example of a radiology workflow with a cloud-based AI server installed.
Hybrid AI Nodes
However, there are other AI software integration options that minimize the downsides of the previous examples. These hybrid AI Nodes are AI servers that can be installed onsite, connected to the clinical facility’s network, or on an external cloud.
The AI node also allows for integration with PACS systems, with automatic forwarding from the PACS in place, the software pre-processes the MRI right after scanning. The results will be ready for when the radiologists want to check and validate results before a standardized and easy-to-communicate report will be created at the end of the reading process and will be sent back to PACS from the AI Node Platform.
An onsite AI Node is a better option than installing the AI software in a separate workstation as the node allows radiologists to access the AI software from different locations of the same hospital or clinical facility (as long as they stay inside the hospital network). Additionally, several radiologists can access the software and assess their own scans at the same time.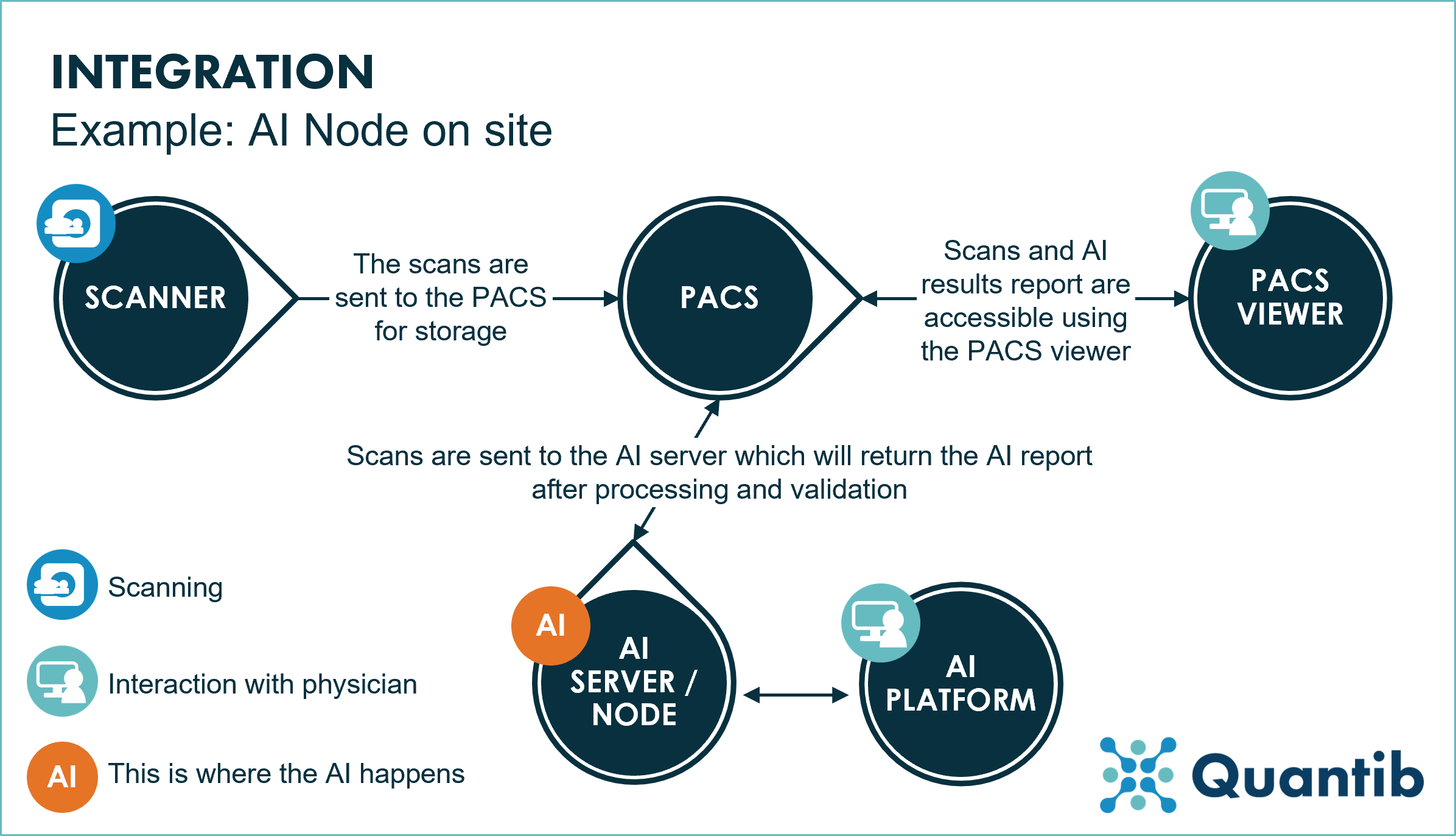
Figure 3: An example of a radiology workflow using an on-site AI Node.
When compared to a fully automatic software placed on an external cloud, an internal node gives the control back to the radiologist while supporting the most tedious parts of the assessment, like segmentations or volumetry calculations. Apart from that, the assessment of the scan can be done in real time, in a way that radiologists don’t have to wait long minutes or even hours before receiving the AI results.
Besides that, having the software stored on an external cloud has its benefits. In the first place, the clinic does not have to take care of updating the physical server or dealing with its technical issues. Moreover, opting for an external cloud will save the clinic money, as they do not have to deal with the costs of maintenance of the physical server.
Do bear in mind that, if the AI Node is installed on an on-site node or server, radiologists may need to connect to a VPN to access it from outside of the clinic. However, that is not needed when logging into the software stored on an external cloud, saving the radiologist a step in their workflow.
An example: Quantib AI Node
Quantib AI Node is our preferred integration method. It allows us to install our products on a node or server placed onsite, or in a node on an external cloud, where it is protected by Quantib Connect, a product that ensures the encryption and security of all data transmitted to the Node. At the same time the Quantib AI Node allows the user to have easy access to Quantib’s other AI solutions. 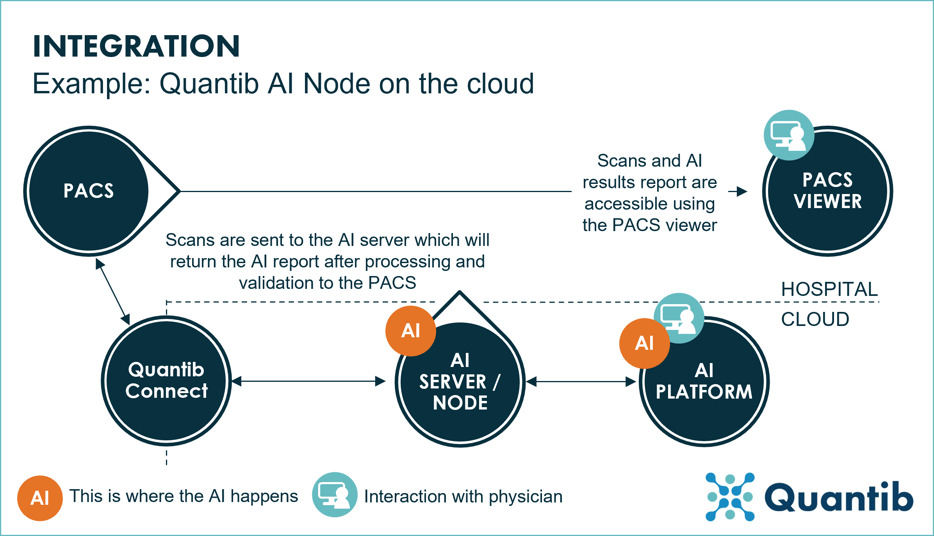
Figure 4: An example of a radiology workflow using Quantib AI Node on the cloud.
Tips for seamless integration
What more can you do to set the integration of your new AI radiology software for success?
In the first place, the AI vendor might need specific and technical information from the clinical facility in order to finish the installation and ensure the proper function of the software. Therefore, having streamlined communication and make sure of providing the right information at the right time will make the installation process shorter and smoother.
Once the software is up and running, the team of radiologists still needs to get used to the software and the interface. For that, make sure the whole team, both radiologists and IT personnel involved with installation and maintenance, get the proper training on the software, so they know how to use it and how to react whenever there is a problem. Lastly, as we mentioned before, provide every professional that will interact with the software a direct line of contact with the service department of the AI vendor so that they can always be available to help out in case something is not working properly or does not respond the way it was expected to.
Conclusion
Every integration option has its benefits and its disadvantages. An onsite integration may give the clinic more control over their data, however, an external cloud provides generally more flexibility for the users.
We recommend choosing the option that will integrate better with the pre-existing radiology workflow. When in doubt, always make sure to get in contact with the AI radiology vendor that offers the solution fitting your clinical challenge in the best way and go over all the possible options of the integration process.
Would you like to know more about which products can you introduce in your clinic through Quantib AI Node and Quantib Connect? Check out our solutions.