Learn more about publications and scientific research involving Quantib.
Quantib ND Quantib Prostate Quantib's Algorithm for Body Composition Quantib BrainArtificial Intelligence for Neuroimaging and Musculoskeletal Radiology: Overview of Current Commercial Algorithms
Berson et al.,
Seminars in Roentgenology, 2023
-
Quantib® ND and Quantib® Brain are listed as existing FDA-approved AI products in neuroimaging in this review.
-
The article mentions that these AI products are easily integrated with clinical workflow and can automate and generate quantitative data from brain MRI in minutes of image acquisition, and therefore guiding neurologists and neurosurgeons in their daily practice
Combining semi‑quantitative rating and automated brain volumetry in MRI evaluation of patients with probable behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia: an added value for clinical practise?
Calloni et al.,
Diagnostic Neuroradiology, 2023
-
The study set out to evaluate whether combining semiquantitative and quantitative assessment of brain atrophy would add value in clinically diagnosing the behavioural-variant of frontotemporal dementia (bvFTD). A general trend of higher accuracy in diagnosing bvFTD was observed, when using the semiquantitative assessment alone, or combining both.
-
Quantib® ND was used as one of the methods to perform automated quantitative atrophy assessment.
Twenty-four hour blood pressure variability and the prevalence and the progression of cerebral white matter hyperintensities
Starmans et al.,
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 2023
- This longitudinal study investigated the relationship between blood pressure variability (BPV) and progression of cerebral white matter hyperintensities (WMH). Higher 24-hour and daytime diastolic average real variability (ARV) was associated with more progression of WMH during two years of follow-up.
- In this study, Quantib® ND was used to determine WMH volume.
Longitudinal Brain Atrophy Rates in Presymptomatic Carriers of Genetic Frontotemporal Dementia
Poos et al.,
Neurology, 2022
- This study investigated longitudinal brain atrophy rates in the presymtomatic stage of genetic frontotemporal dementia (FTD) using Quantib® ND.
- Between different gene groups, affected brain regions and the age at which atrophy rates start to accelerate diverge from the normal aging slopes, highlighting the value of normative volumetric software for disease tracking and staging in genetic FTD.
Comparing two artificial intelligence software packages for normative
brain volumetry in memory clinic imaging
Zaki, Vernooij, Smits, Tolman, Papma, Visser, Steketee.
Neuroradiology, 2022
- This study compares diagnostic reports from two AI software packages and show high inter-rater agreement and high accuracy and sensitivity when distinguishing normal and abnormal profiles.
- Radiological assessment of the MRI results, clinical profile and an understanding of the software used are needed for correct diagnostic interpretation, as results from software packages are not interchangeable.
How Machine learning is embedded to support clinician decision making: an analysis of FDA-approved medical devices
Lyell, Coiera, Chen, Shah, Magrabi.
BMJ Health & Care Informatics, 2021
- This study reviews the use in clinical practice, the benefits, the consequences and the possible risks of FDA cleared devices that use machine learning (up to early 2020).
- In this study, Quantib® ND and Quantib® Brain were are reviewed as assistive machine learning devices for quantification.
Distinctive pattern of temporal atrophy in patients with frontotemporal dementia and the I383V variant in TARDBP
Mol et al.,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 2021
- This study examines the genetic cause of frontotemporal dementia and finds a distinctive pattern of temporal atrophy in patients with one specific gene-variant.
- In this study, Quantib® ND was used for quantitative assessment of volume loss across lobar brain regions.
AI in de Neuroradiologische praktijk. Een aanzienlijke verandering en verbetering
Prof. Smits.
Memorad, Nedelandse Vereniging voor Radiologie, 2021
- Commentary on Quantib® ND, and its usefulness in clinical practice (in Dutch).
Overview of MR Imaging Volumetric Quantification in Neurocognitive Disorders
Raji, Ly, Benzinger.
Topics in Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2019
- This study reviews the history and methods for volumetric quantification, as well as acquisition protocols for multiple cognitive disorders.
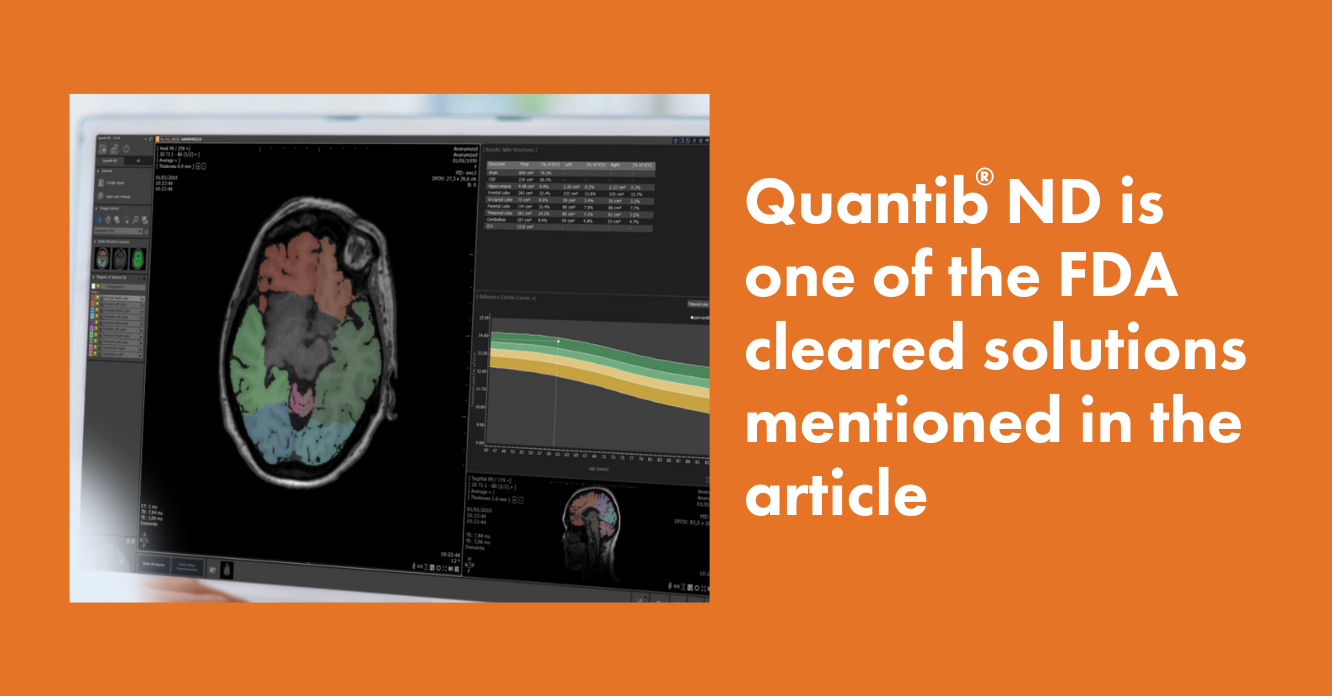
- In this study, Quantib® ND is listed as one of the FDA cleared software solutions.
Aortic stiffness and brain integrity in elderly patients with cognitive and functional complaints
Tap, van Opbroek, Niessen, Smits, Mattace-Raso.
Clinical Interventions in Aging, 2018
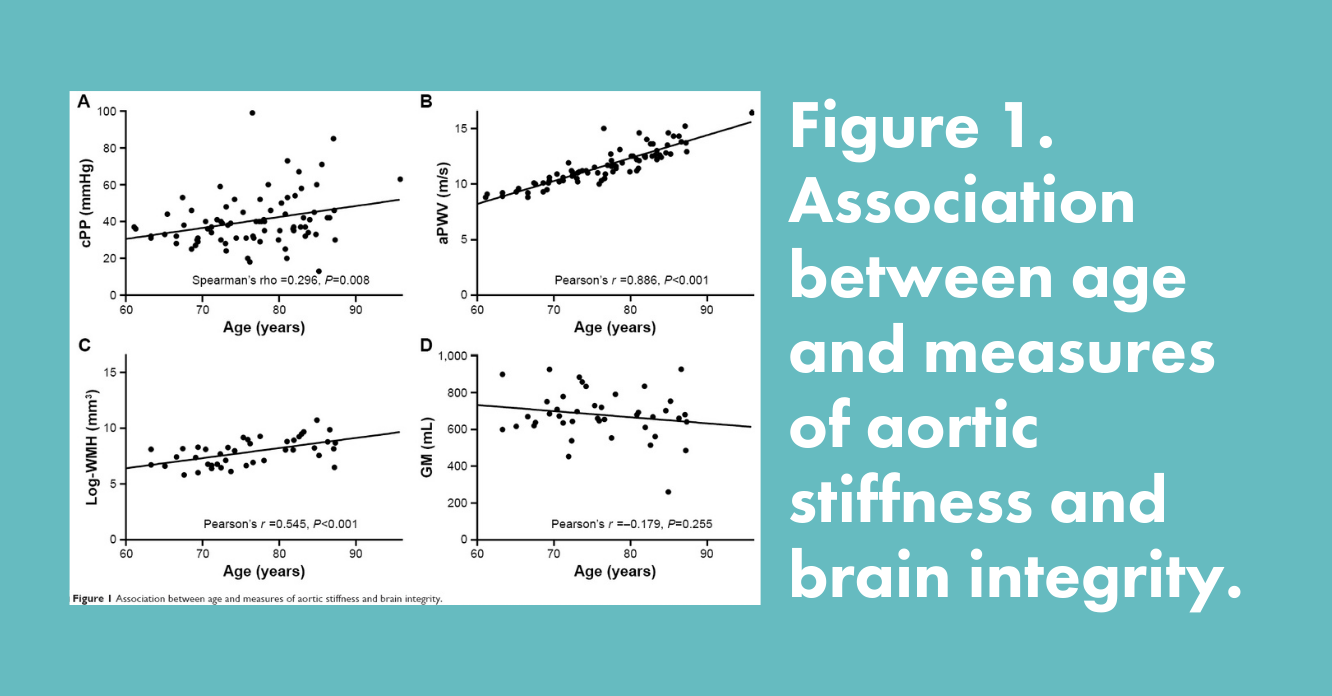
- This study shows a partial association between higher aortic stiffness and increased volume of WMH and decreased volume of grey matter in older patients with cognitive and functional complaints.
- In this study, Quantib® ND was used to segment brain tissue, and WMH.
Gray matter heritability in family-based and population-based studied using voxel-based morphometryortic
Van der Lee et al.,
Human Brain Mapping, 2017
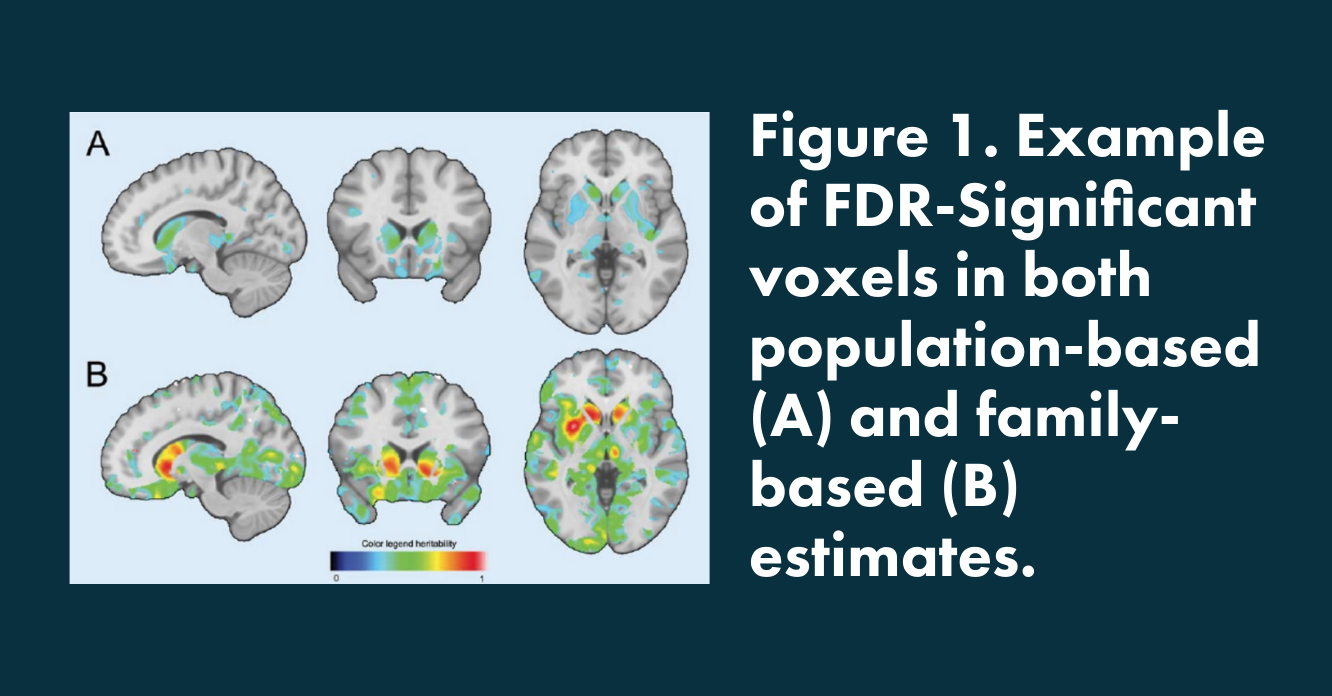
- This study looks at the influence of the genetics on gray matter heritability and showed that construction of reliable heritability maps of gray matter voxels is feasible.
- In this study, Quantib methods were used for brain tissue segmentation.
Automatic tissue segmentation of head and neck MR images for hyperthermia treatment planning
Fortunati et al.,
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 2015
- Fortunati et al. investigate atlas based segmentation combined with a local intensity based classification algorithm for segmentation of different brain structures.
- Quantib™ ND uses the same method for its hippocampus segmentation.
Accuracy and reproducibility study of automatic MRI brain tissue segmentation methods
de Boer et al.,
NeuroImage, 2010
- De Boer et al. investigate several methods for follow-up analysis of brain structure segmentations.
- Quantib™ ND brain segmentation algorithm uses the automatically trained kNN classifier.
White matter lesion extension to automatic brain tissue segmentation on MRI
de Boer et al.,
NeuroImage, 2009
- De Boer et al. describe the underlying methods used for the Quantib™ ND algorithm development of the Quantib™ ND brain structure segmentation and white matter hyperintensity segmentation as included in Quantib™ ND.
- For further reading we refer you to the PhD thesis of Renske de Boer, the product owner of Quantib ND.
Quantib® Prostate
Retrospective analysis of radiotherapy plans for prostate cancer after revision of MRI targeted lesions detected by Quantib
Petrucci et al,
Annual Meeting of the Italian Society of Uro-Oncology (SIUrO), 2023
- Retrospective evaluation coverage of therapy plans in 5 subjects with prostate cancer who underwent hypofractionated radiotherapy.
- These preliminary results showed that Quantib can assist the identification of target lesions, and confirmed optimal radiotherapy coverage of the target volume and a subsequent biochemical response at minimal follow-up.
Bridging the experience gap in prostate multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging using artificial intelligence: A prospective multi-reader comparison study on inter-reader agreement in PI-RADS v2.1, image quality and reporting time between novice and expert readers
Forookhi et al.,
EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF RADIOLOGY, 2023
- The study investigated the impact of using Quantib® Prostate on inter-reader agreement in PI-RADS scoring at various levels of image quality and reader confidence among novice readers.
- For less experienced readers, using Quantib® Prostate improved the inter-reader agreement and the diagnostic accuracy. The researchers concluded that using Quantib, along with PACS, can benefit less experienced readers, especially when image quality and reader confidence are low.
Biparametric prostate MRI: impact of a deep learning-based software and of quantitative ADC values on the inter-reader agreement of experienced and inexperienced readers
Cipollari et al.,
La radiologia Medica, 2022
- This study investigated the use of Quantib software on inter-reader agreement, diagnostic performance, and reporting times of biparametric MRI for experienced and inexperienced readers.
- Their conclusion state that Quantib Prostate allows the radiologist to achieve slightly higher inter-reader agreement with mpMRI, compared to just interpreting bpMRI sequences, both in the case of experienced and inexperienced readers.
“Artificial intelligence” (Quantib®Prostate) to improve cancer detection in transperineal MRI/ultrasound fusion biopsies of the prostate – The next game changer?
Günzel et al.,
ESUR conference presentation, 2022
- This prospective analysis evaluates the detection and localization of PCa by Quantib in 150 patients when performing transperineal mRI/ultrasound fusion biopsies of the prostate.
- The use of AI software to evaluate mpMRI before MRI-TRUS-TPBx could improve PCa detection and localization. The Urologist using Quantib detected all clinically relevant PI-RADS index lesions, and 10 PCa not detected by initial radiology reading without AI software.
Software-basierte „Künstliche Intelligenz“ (Quantib® Prostate) zur Evaluierung von multiparametrischen MRT – Kann die Prostatakarzinomdetektion bei transperineale MRT/Ultraschall-Fusionsbiopsien der Prostata (MRI-TRUS-TPBx) dadurch verbessert werden?
Günzel et al.,
DGU conference presentation, 2022
- Prospective evaluation of 62 patients sent for biopsies based on radiologic findings from 7 different centers.
- 95 suspicious lesions were identified by the radiologist, and 129 by the AI-assisted urologist. PCa detection rate went from 61% to 66% with Quantib, with only a slightly higher false positive rate.
Quantib Prostate Compared to an Expert Radiologist for the
Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer on mpMRI: A Single-Center
Preliminary Study
Faiella et al.,
Tomography, 2022; ECR overture poster presentation, ECR 2022
- This study compared radiology reports from one expert radiologist between 2019 and 2020 with the reports from an inexperienced first-year radiology resident aided by Quantib Prostate.
- They showed that Quantib Prostate can be a supporting tool to untrained radiologists, as well as increase sensitivity and positive predictive value in PCa diagnosis.
An AI-powered radiomics model for the detection of extraprostatic extension
Van den berg et al.,
ISUI conference presentation 2021
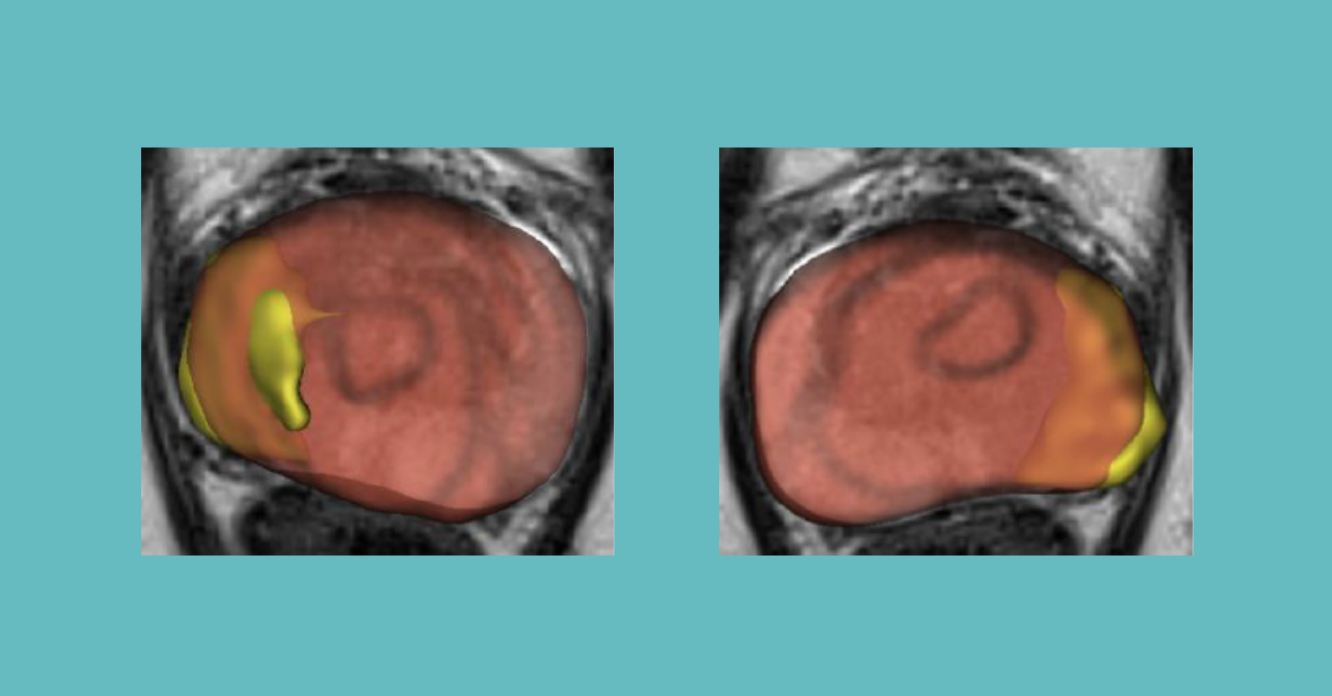
- Won best abstract award
- This work assessed new radiomic features for the prediction of extraprostatic extension (EPE) on lesion level using artificial intelligence.
- The AI-powered radiomics model achieved good diagnostic discrimination for lesion-specific EPE prediction, with lesion volume and tumor contact volume being most predictive.
Effect of varying DWI b values on prostate lesion segmentation accuracy and robustness
Postigo Filiquete et al.,
ESMRMB conference presentation 2021
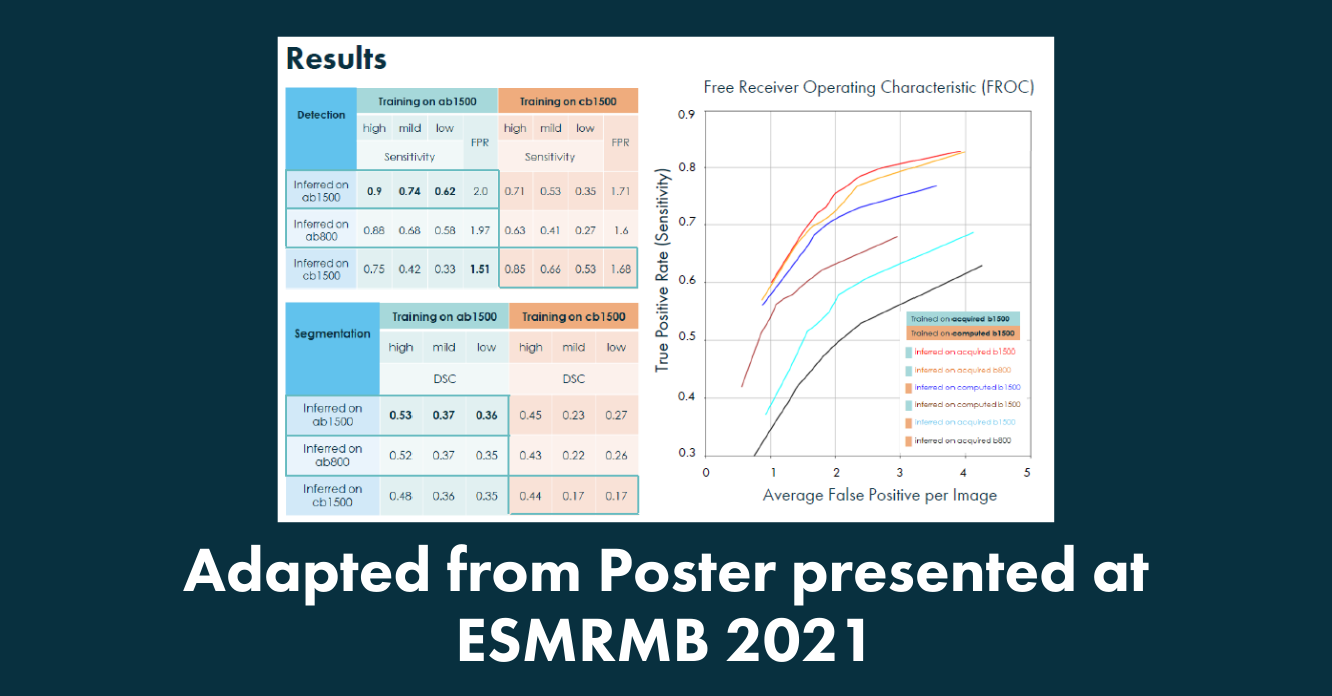
- They investigated prostate lesion segmentation accuracy by training a segmentation network using acquired DWI (aDWI) or computed DWI (cDWI) at different b values.
- The results showed, best segmentation accuracy with a network trained and tested with high b values (b1500), robustness against different b values during training, and a general finding that lesion segmentation networks are less sensitive to different measured b values, than to computed higher b values.
Quantib AI algorithm for Body Composition
Dynamic anthropometrics: sarcopenia and survival in pancreatic cancer
Yee et al.,
Society for Surgical oncology meeting PResentation, 2023
- Quantib's Body Composition was used to study the development of sarcopenia over time during neoadjuvant therapy.
- The study showed that patients who develop sarcopenia during NAT have worse survival, and are less likely to receive adjuvant therapy, without worse perioperative complications.
Pediatric body composition based on automatic segmentation of computed tomography scans: a pilot study
Samim et al.,
Pediatric radiology, 2023
- This study aimed to evaluate automatic segmentation for body composition on pediatric computed tomography (CT) scans and to provide normative data on muscle and fat areas throughout childhood using automatic segmentation.
- Quantib body composition allows for accurate quantification of pediatric body composition.
Comparison of CT Scan and Bioimpedance Spectroscopy for Fat Free Mass Measurements in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
Visser et al.,
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation, 2023
- This study calculated fat free mass (FFM) and lean tissue mass (LTM) derived from bio-impedance spectroscopy (BIS) in 60 patients with chronic kidney disease. These measures were compared with FFM derived from CT as calculated by Quantib Body Composition as ground truth.
- Results of this study showed that FFMbis might be a valid surrogate measure for the estimation of FFM.
Optimizing carboplatin dosing by an improved prediction of carboplatin clearance using a CT-enhanced estimate of renal function
Molenaar-Kuijsten et al.,
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 2023
- This study aimed to assess whether using the CT-enhanced estimate of RenAl FuncTion (CRAFT) formula for calculating creatinine clearance (CRCL) would provide a more accurate prediction of carboplatin clearance, compared to the traditional Cockcroft-Gault formula, which was known to overestimate CRCL in cancer patients withabnormal body composition.
- Quantib Body Composition was used to obtain the radiomics parameters used in the CRAFT formula.
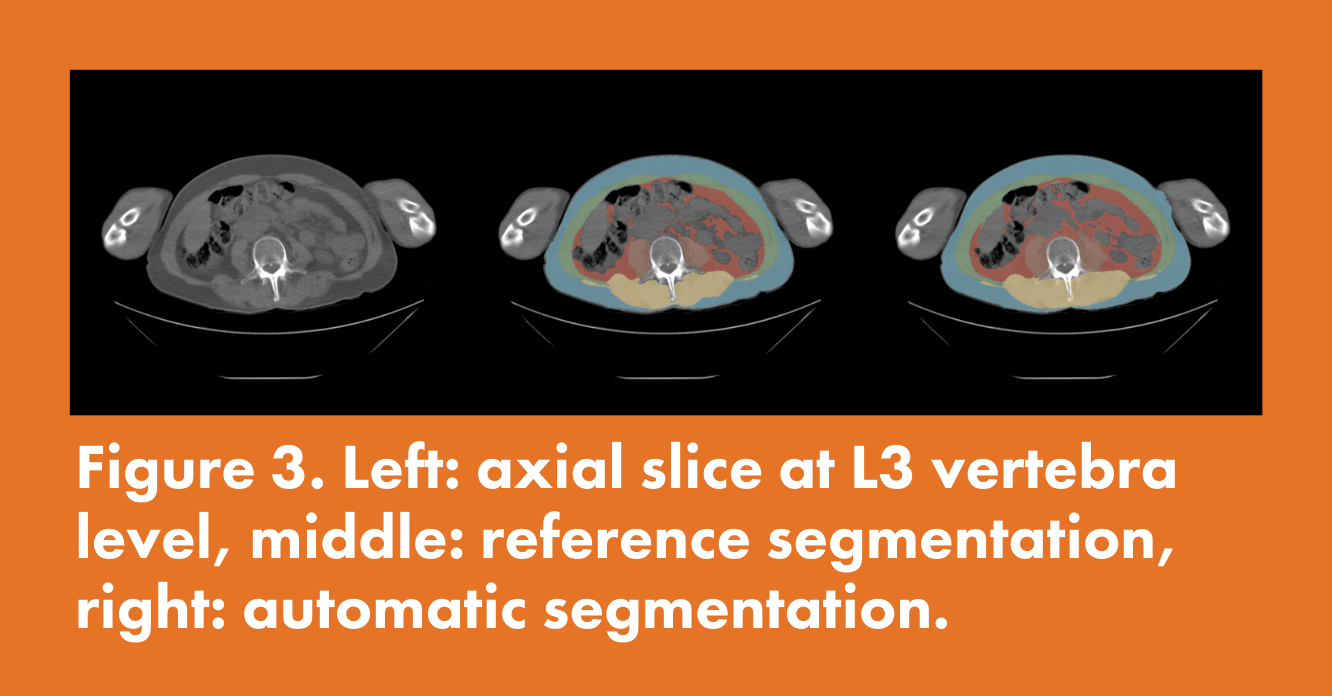
The association of radiologic body composition parameters with clinical outcomes in level‑1 trauma patients
Sweet et al.,
European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery, 2023
- The study demonstrated that, in level-1 trauma patients without severe neurological injuries, automatically-derived body composition parameters can independently predict an increased risk of specific complications and clinical outcomes.
- Quantib Body Composition was used to automatically identify and segment the CT image at the L3 level.
GLIM-based malnutrition, protein intake and diet quality in preprocedural Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) patients
Erck et al.,
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN, 2022

- This study showed a high prevalence of malnutrition among patients with transcatheter aortic valve implantation, and advocates for nutrition interventions for this patient group.
- Quantib Body Composition was used to identify patients with a low muscle mass.
Application of AI Software on CT images for the evaluation of Sarcopenia in Patients with Genitourinary Tumors
Borrelli et al.,
ESUR conference presentation, 2022
- This study utilized our body compositions software to evaluate treatment toxicity and oncology status in patients with genitourinary tumors.
- They found a link between sarcopenia and stable or progressive disease, while no correlation with treatment related toxicity could be established in these preliminary results.
Association of skeletal muscle loss with patient-reported treatment toxicity among colon cancer patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy
Smit et al.,
ESMO congress presentation, 2022
- This study explored if changes in skeletal muscle mass during ACT therapy for colon cancer are associated with patient-reported treatment toxicity.
- Prospective results show that skeletal muscle mass loss up to 3-months post-ACT was associated with an increased risk of patient reported toxicity.
ACCESS the abstract
Do body composition parameters correlate with response to targeted therapy in ER+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer patients? Role of sarcopenia and obesity
Kripa et al.,
Frontiers in Oncology, 2022
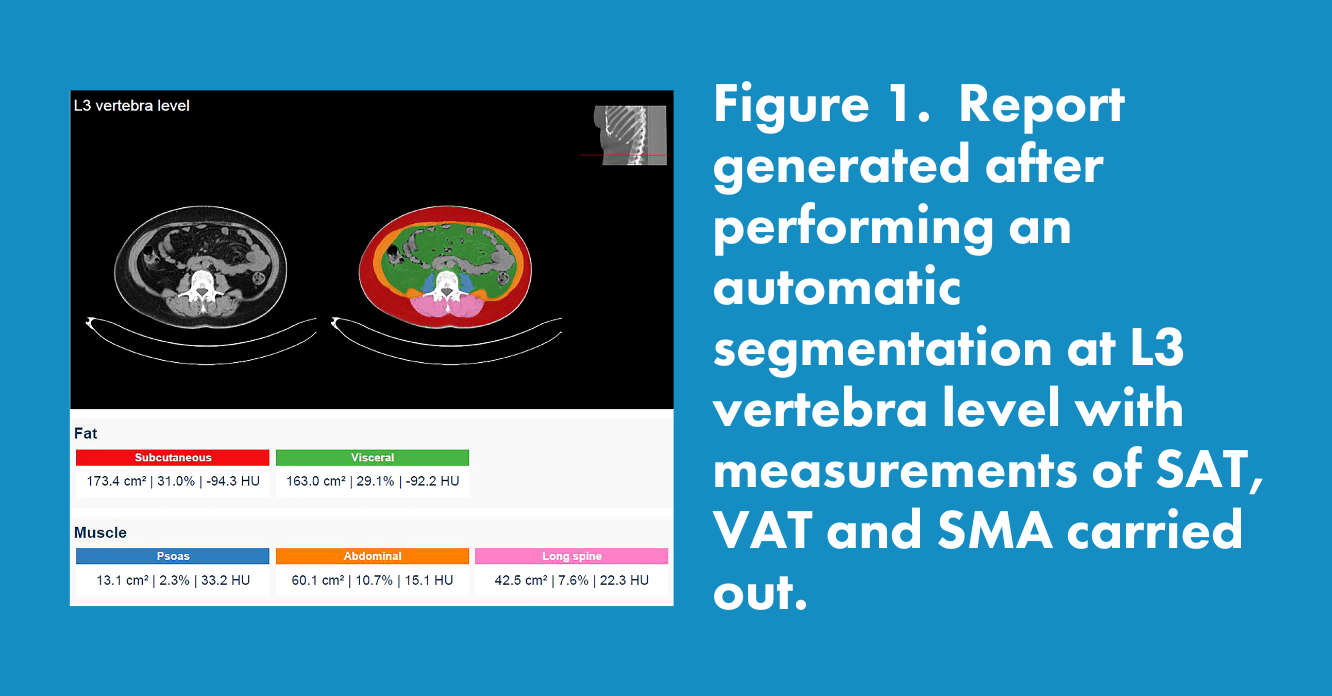
- This study investigated the association between body composition parameters and prognosis in patients with metastatic breast cancer.
- The authors showed a correlation between sarcopenia and progression of disease, and demonstrated that visceral adipose tissue can positively influence the response to targeted therapy.
Exposure–Response Analysis of Osimertinib in EGFR Mutation Positive Non‑Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients in a Real‑Life Setting
Boosman et al.,
Pharmaceutical Research, 2022
- This paper investigates a lung cancer drug (Osimertinib) on exposure efficacy, toxicity, and muscle mass-response relationships.
- The Quantib body composition algorithm was used to identify sarcopenic patients.
The Association between Muscle Quantity and Overall Survival Depends on Muscle Radiodensity: A Cohort Study in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients
van Amsterdam et al.,
Journal of personalized medicine, 2022
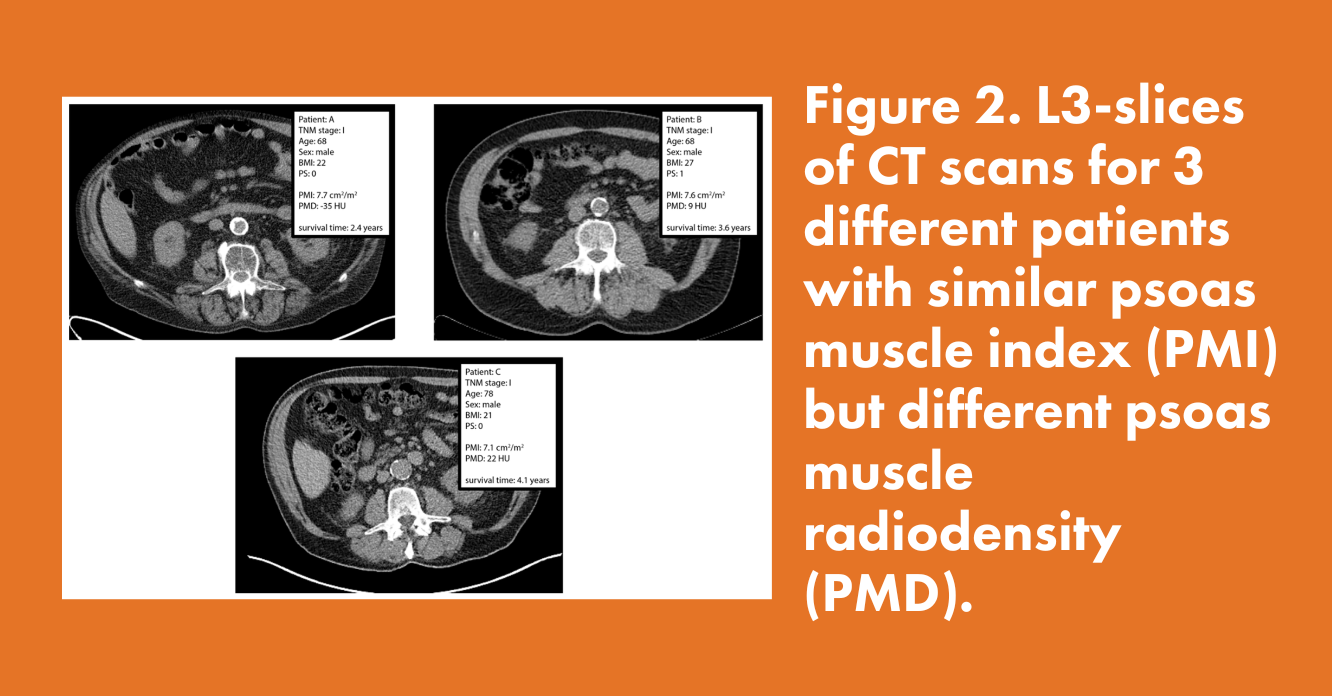
- Survival of lung cancer patients is associated with an interaction between both muscle area and muscle density. High muscle quantity is associated with better overall survival (OS) when muscle radiodensity is higher.
- Quantib Body Composition software was used for the extraction of the psoas muscle index (PMI) and psoas muscle radiodensity (PMD).
Deep learning body-composition analysis of clinically acquired CT-scans estimates creatinine excretion with high accuracy in patients and healthy individuals
Pieters et al.,
Scientific Reports, 2022
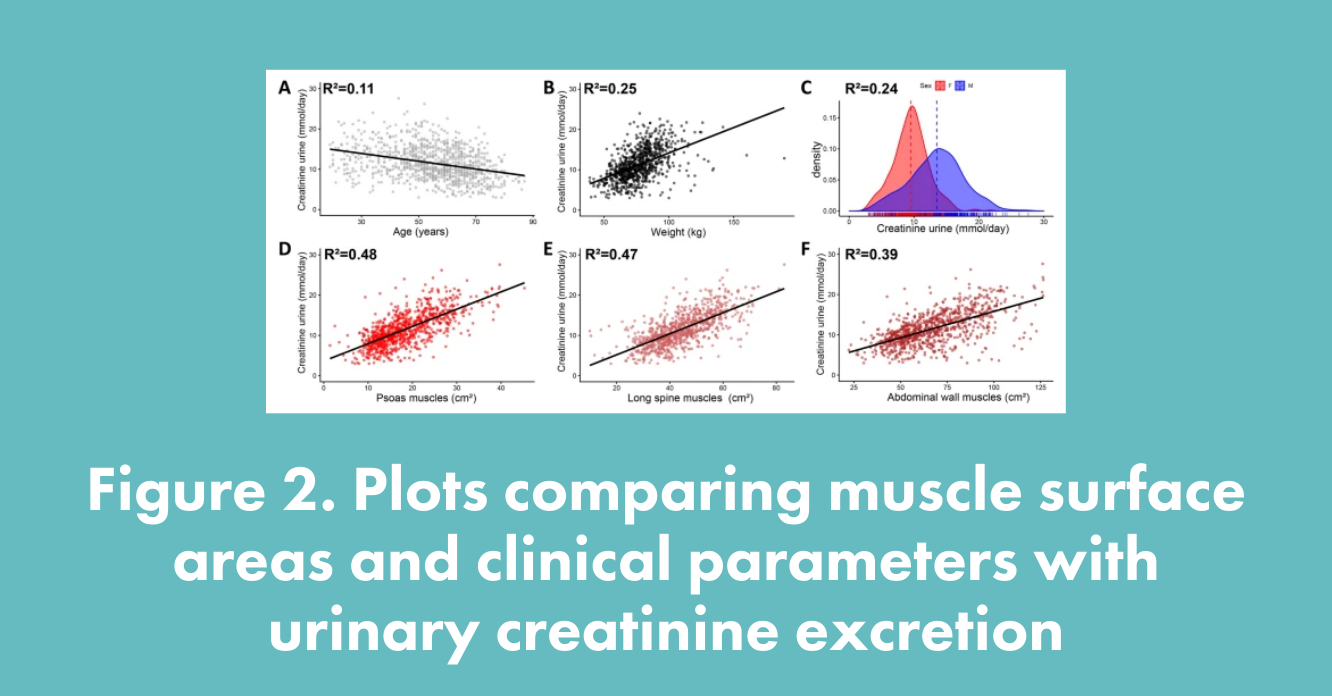
- New automated equations that use the body composition analysis, instead of traditional clinical characteristics, are better at estimating creatine production.
- The authors showed on a large set of data that the proposed method provides an improved estimation of renal function.
Subcutaneous and visceral fat density is associated with long-term mortality after transcatheter aortic valve implantation
Van Erck et al.,
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, 2022
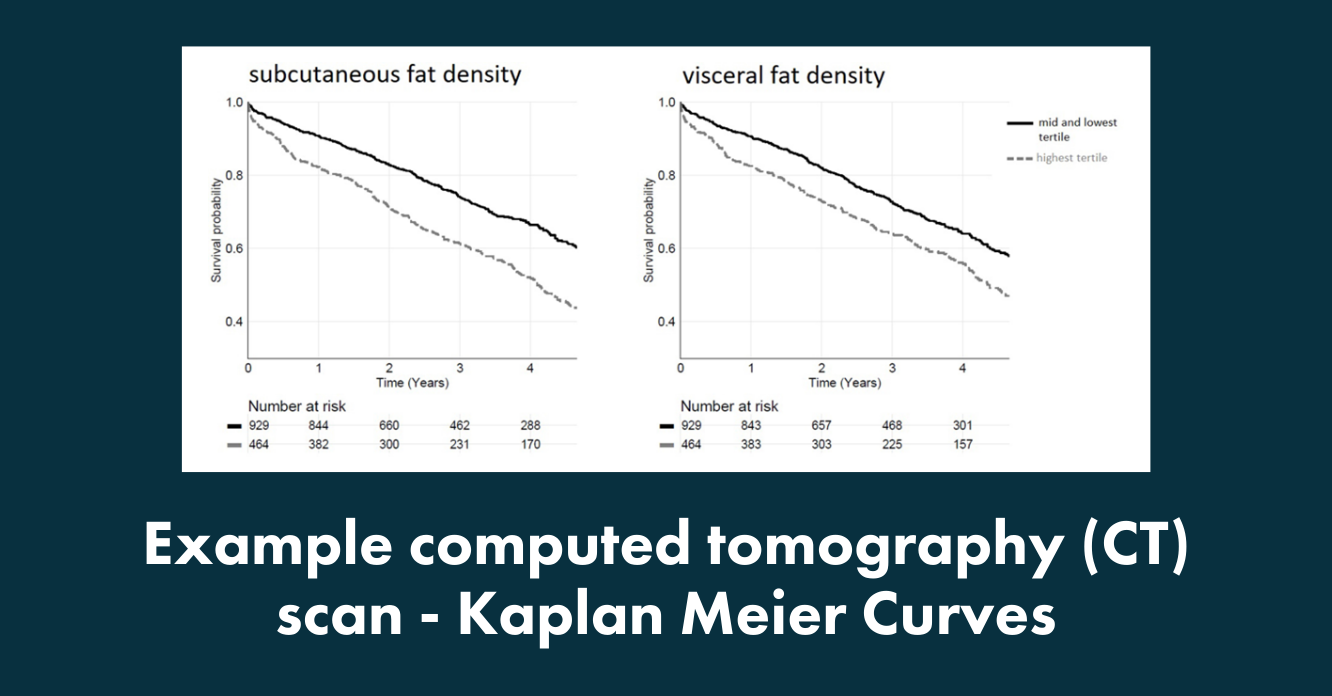
- Despite a technically successful procedure, not all patients with severe aortic valve stenosis benefit from Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI).
- The authors show that the density of subcutaneous and visceral fat is associated with mortality in TAVI patients. These results show that future risk models in TAVI patients should take fat density into account.
Evaluation of a fully automatic deep learning-based method for the measurement of psoas muscle area
Van Erck et al.,
FRONTIERS IN NURITION, 2022
- The study evaluates if fully automatic DL methods can substitute manual psoas annotation, for the assessment of muscle mass. Manual segmentation is cumbersome and time consuming but has shown to be a good marker for malnutrition, sarcopenia, and adverse outcomes.
- Assessment with Quantib Body Composition software demonstrates accurate performance and is a reliable tool that offers great opportunities for analysis in large scale studies and in clinical applications.
Towards personalized contrast injection: artificial-intelligence-derived body composition and liver enhancement in computed tomography
De Jong, Veldhuis, Wessels, de Vos, Moeskops, Kok.
Journal of personalized medicine, 2021
- This study shows that contrast injections should be personalized. Liver enhancement is more strongly associated with the percentage of lean body weight than with total body weight or body mass index.
- In this study, Quantib’s AI algorithm for body composition was used to segment and determine the body composition and calculated percentages of lean body weight.
Automatic quantification of body composition at L3 vertebra level with convolutional neural networks
Moeskops, de Vos, Veldhuis, de Jong, Išgum, Leiner.
ECR 2020 conference poster
- Investigation of feasibility of a deep learning-based method for automatic segmentation of fat, visceral fat, psoas muscle, abdominal muscle and long spine muscles at the level of L3
Automatic Quantification of 3D Body Composition from Abdominal CT with an Ensemble of Convolutional Neural Networks
Moeskops et al.,
RSNA 2019 conference pRESENTATION
- This study shows that accurate fully automatic segmentation of subcutaneous fat, visceral fat and psoas muscle from full abdominal CT scans is feasible.
- The proposed method allows fast and fully automatic analysis of 3D body composition in abdominal CT that can aid in individualized risk assessment in cardiovascular disease and cancer.
Quantib Brain
Circulating angiopoietin-2 and angiogenic microRNAs associate with cerebral small vessel disease and cognitive decline in older patients reaching end-stage renal disease
Bijkerk et al.,
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation, 2022
- This study set out to determine the levels of ADMA, Ang-2 and angiogenic miRNAs and their association with brain MRI markers of small vessel disease (SVD) and cognitive impairment in older patients reaching end-stage renal disease. Ang-2 and miRNA levels were found to be associated with SVD and impaired cognition.
- Quantib® Brain was used to determine white matter hyperintensity (WMH) volume, an MRI marker of cerebral SVD, as well as intracranial volume.
Accuracy of the compressed sensing accelerated 3D-Flair sequence for the detection of MS plaques at 3T
Mangesius et al.,
Biomedicines, 2022
- To date, there is no gold standard to quantify brain atrophy in clinical practice; many available methods show high internal consistency but have rarely been evaluated against each other.
- This study recognizes that there are significant differences between segmentation methods and their underlying segmentation protocols, different software applications therefore cannot be used interchangeably.
Qualitative and Quantitative Comparison of Hippocampal Volumetric Software Applications: Do All Roads Lead to Rome?
Toledano-Massiah et al.,
American Journal of Neuro-Radiology, 2018
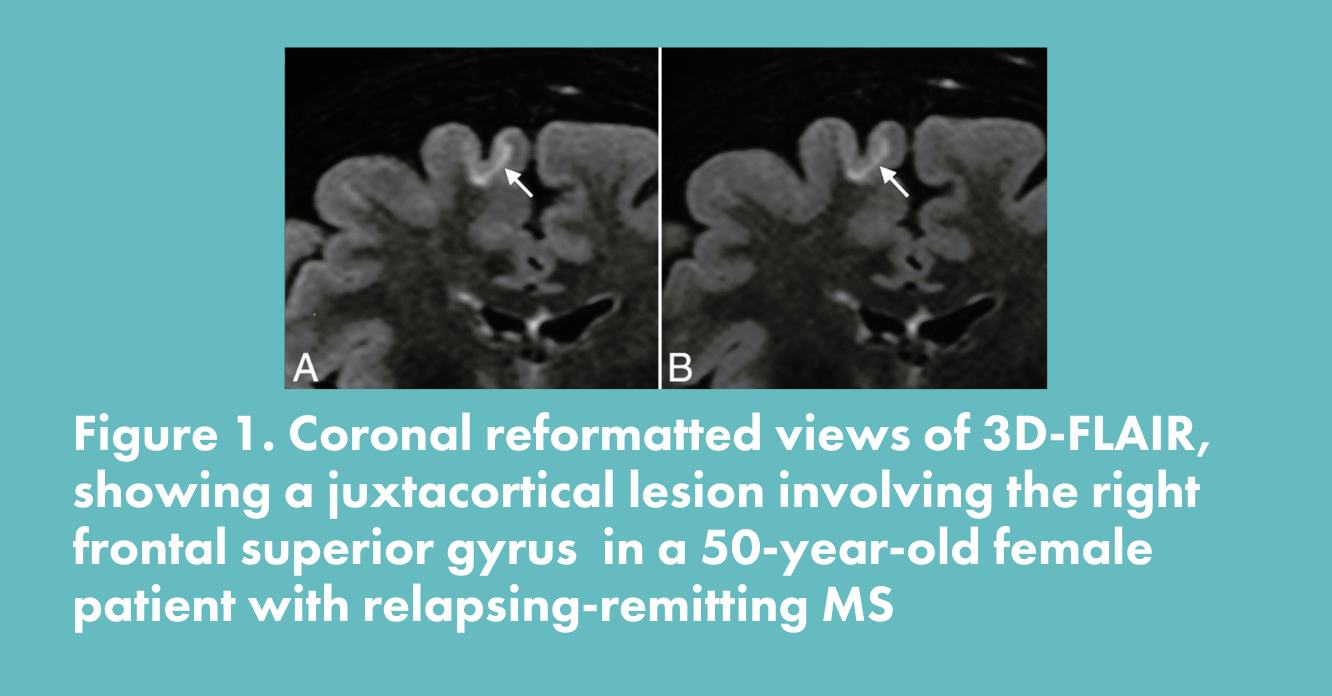
- The authors evaluate the diagnostic performance for the detection of MS lesion of 3D-Flair sequences without and with compressed sensing. Diagnostic performance is preserved with faster acquisition in compressed sensing of 3D-Flair sequences.
- In this study, Quantib Brain was used to quantify the volume and total number of MS lesions on both Flair sequences.
Curious for more detailed info on Quantib® Prostate or Quantib® ND?
We are happy to schedule a call and give you the full tour of the solutions during a video conference.
.png?width=1332&name=Thumbnails%20-%20scientific%20resources%20(1).png)